Description
Geography
Cultural
aspects
Biodiversity
Main
attractions
Activities
allowed
Existing
facilities
Documents and
recommendations
How to get?
For many years it was suspected that the coastline and the marine environments found in front of the towns of Galera, Estero de Platano, Quingue y San Francisco- located on the south-west area of the Esmeraldas province – contained a biological diversity comparable to that found in the waters of the Galapagos islands. The suspicion was confirmed in the year 2008 after several years of work by different entities. As a result of this work, and the active participation of the local community, it was declared the first continental Ecuadorian marine reserve.

From Quito. Access to this area is reached through the route Quito-Calacali-La Independencia-Esmeraldas (314 km) or the route Quito-Sto. Domingo- Esmeraldas (322 km); on the entrance to the city of Esmeraldas you take the route toward Atacames (19 km) and continue until you reach Tonchigue. Here detour to the right until you reach the Galera town. The asphalt road continues until you reach the town of Quingue, from here for about 12 kilometres the road is not very well maintained. The most used means of public transportation here are the Pacific and River Taviazo bus companies. It can also be accessed by sea through Atacames, Sua or Muisne.
Av. Principal y Malecón, In front of the Gruta de la Virgen del Carmen. Galera. Provincia de Esmeraldas.
There is no telephone on the reserve. For more information contact the Provincial District Environmental Ministry offices at (06) 246-4605.

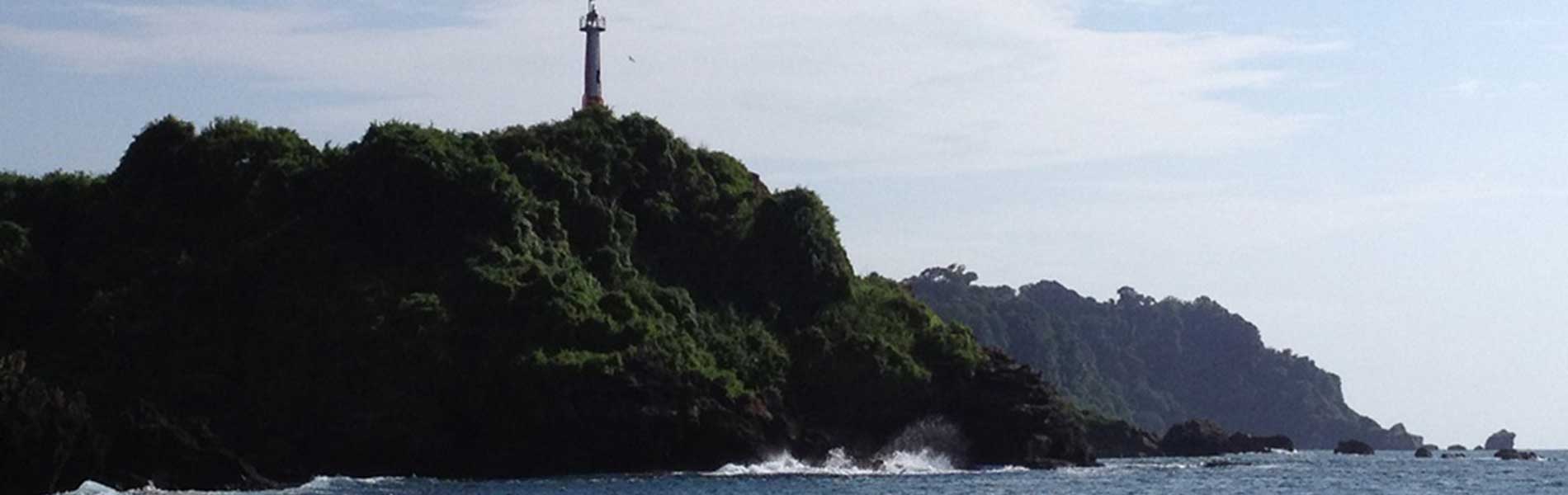
The reserve is located between the coves of Atacames in the north and of Mompiche in the south. The marine area – the main reason for this reserve- includes the shallow waters of the continental shelf, up to depths of 800 metres, where the sunrays no longer reach. This area is one of the few places on the continental Ecuadorian coast where you can find waters 200 metres deep very close to the shore, indeed, only 11 kilometres offshore.
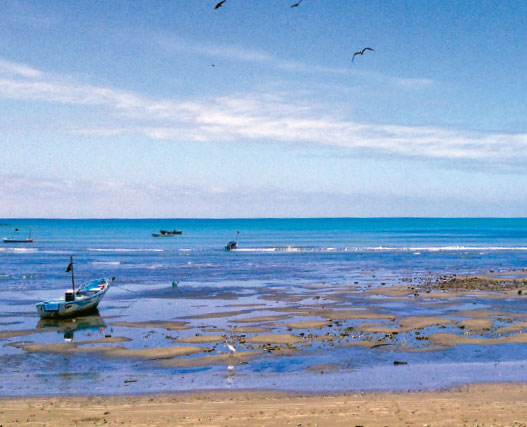

The best way to visit the marine area is through locally guided boat tours. Ruta Maritima Galera-San Francisco; here you can observe sea birds and go deep sea or line fishing. You must be accompanied by a local tour guide.

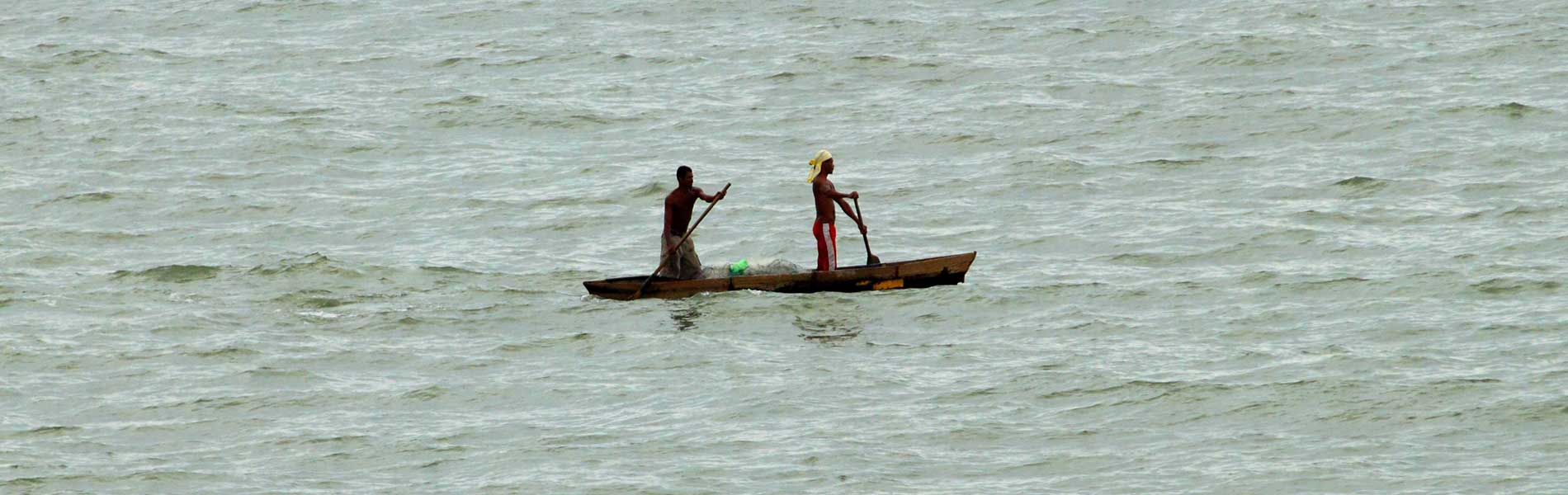
Surrounding the reserve there are several fishing cove towns: Galera, Estero de Platano, Quingue and San Francisco. The most important of these are Galera and San Francisco, where the majority of the area's total catch is found. Most fish are sold in local markets, mainly in Muisne, Atacames, Sua, and Esmeraldas. One of the area's biggest advantages is that on its establishment, the local communities that surround this area became very actively involved. This marine reserve is one of four that exist in the country; all of them are important due to their abundance of fish and invertebrates, as well as for the function they serve in becoming refuges of reproduction and population recovery for various species with commercial value.
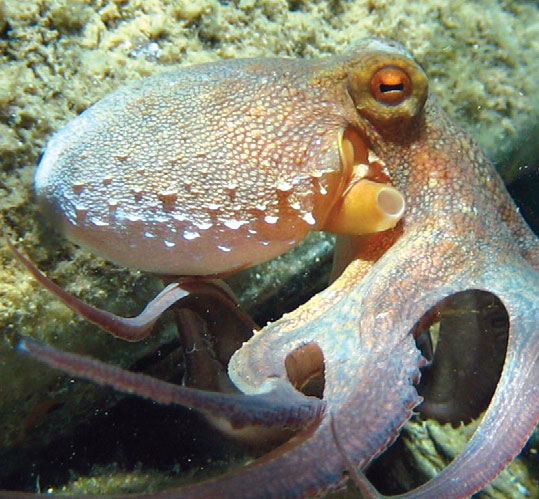

The reserve protects three types of ecosystems: marine, coastal, and estuarine.
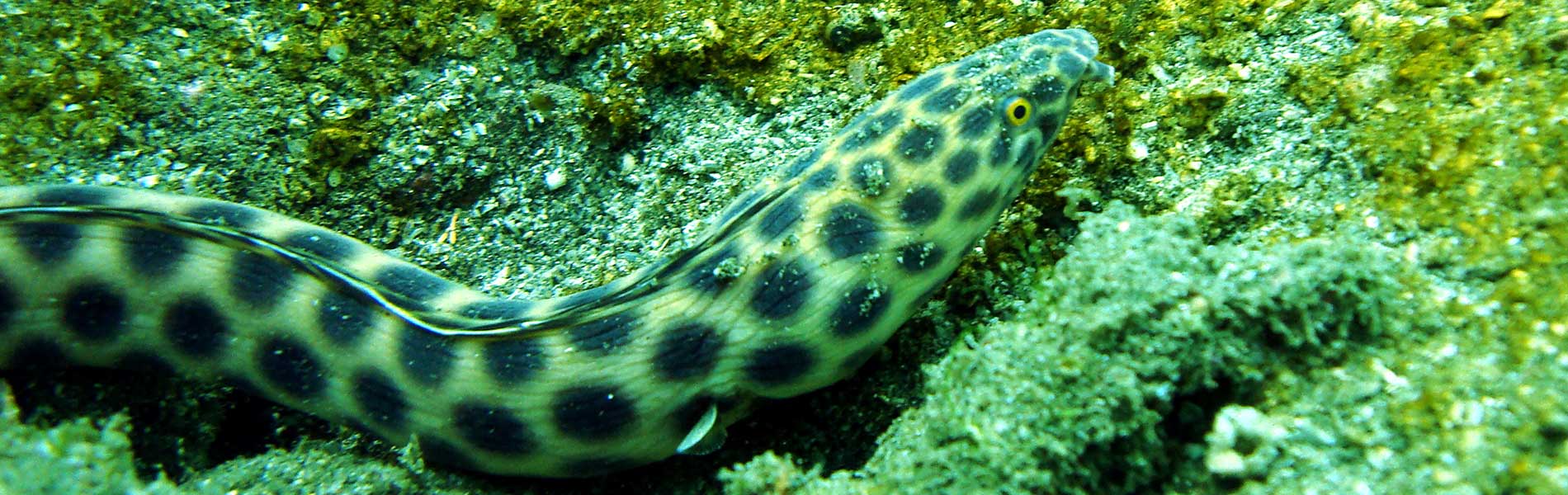
Marine Ecosystems. Rocky and coral reefs in with deep water environments are without a doubt their defining feature. The reefs’ highlights are their extraordinary biodiversity and the fact that they are home to the most important community of black coral on continental Ecuador. Some of the fish found in this area are the angel of Cortez, the hunchback parrot, yellow snapper, royal angel, croaker and rock seabass. Among marine mammals you may find bottlenose dolphins or porpoise, spotted dolphins, short-nosed dolphins and humpback whales; humpback whales reach the coasts of Ecuador between June and September each year.
Coastal Ecosystems. These are cliffs and the different type of beaches that are within the reserve. These are recorded nesting areas of four species of sea turtles: leatherback, hawksbill, green and olive ridley. In the intertidal zone, which is the area that is uncovered when the tide is low, you may see octopus, sea urchins, starfish and small snails.
Estuarine Ecosystems. These include the estuary of Galeras and of the rivers San Francisco and Bunche. The estuarine environments that have developed here are ideal for growth of the mangrove.

Sand beaches and tidepool beaches
More than half of the 37 kilometres on the coast line that the reserve has belong to sand beaches. These can be accessed by a route that runs through the towns of Galera, Estero del Platano, Quingue, Caimito y Cabo San Francisco. In all of these towns there are beaches that are not just beautiful, but also nesting sites for sea turtles, which is why tourism must respect the protection standards of its nesting sites. In the towns of Estero de Platano and Quingue, there are rocky beaches that can be explored during low tide, in each tide pool there is a small underwater world where you may find octopus, sea urchins, anemones, sea lilies, churros and small fish.
Humpback Whales
Each year, between the months of June and September, the appearance of the whales make the area an wonderful option. The whales reproduce in front of the Ecuadorian beaches, and their presence can be enjoyed by tourists.


Clothing. Light clothing and comfortable shoes for the boat rides.
What to Bring. Sun block, insect repellent, camera and/or binoculars, and enough drinking water.
Boat Rides. You must contact legally recognized fishing associations to go on a fishing trip.







