Description
Geography
Cultural
aspects
Activities
allowed
Existing
facilities
Documents and
recommendations
How to get?
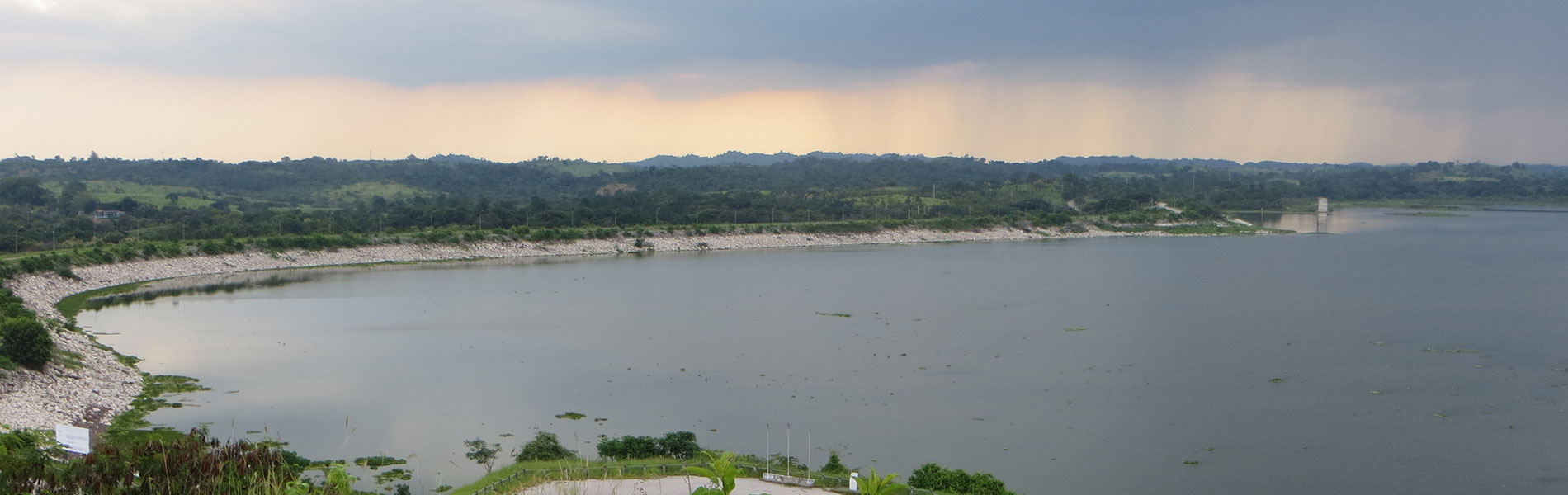
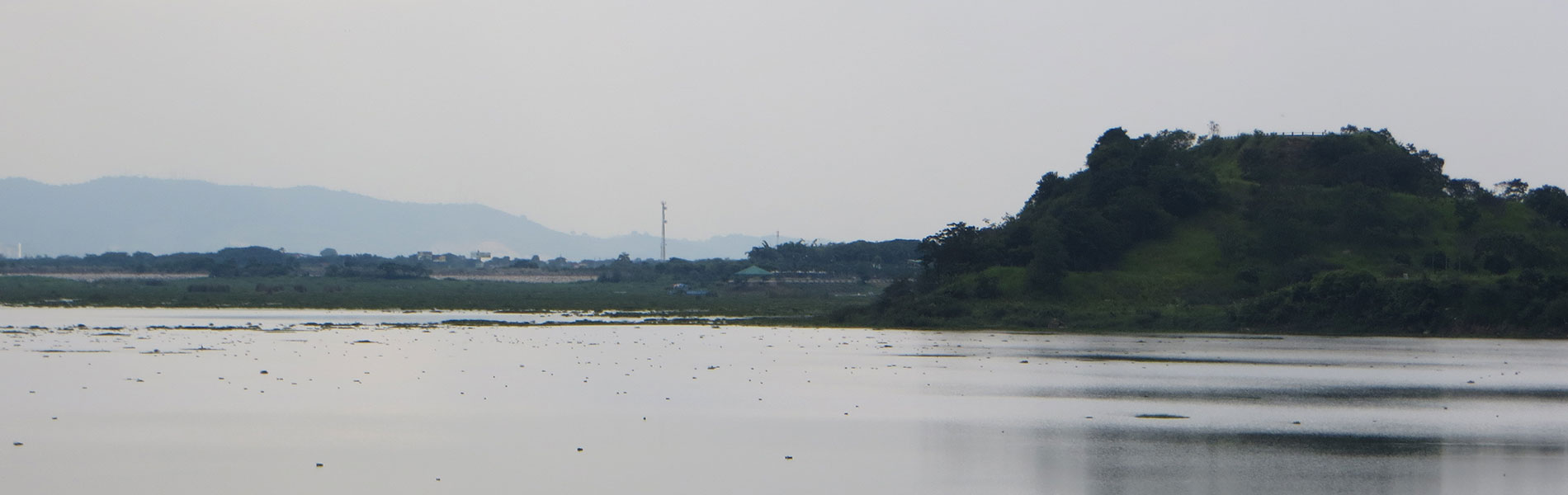
The area is close to Guayaquil city and, as its name suggests, consists of a large artificial lake which is the product of a dam on the river Chongón that maintains a strip of vegetation around of it. The dam was built to divert water for irrigation and human consumption by locals of the Santa Elena peninsula. Subsequently, to take advantage of the landscape created by the dam, the government made it an ecological park with recreational areas. In the area there are several species of native tree to the arid and semi-arid area of the coast including El Amarillo, Balsamo and El Colorado.

From Guayaquil. Admission to the area is located at km 26 of the road Guayaquil - Salinas, two kilometres after the toll. The trip takes 35 minutes by car and one hour by bus. There are also second-order paths that are inaccessible during the rainy season; via Casas Viejas (km 22), via the Cienega – Aguas Negras route and the route that links Fresita and La Teresita (km 30 road Guayaquil - Salinas).
To get more information contact the offices of the Regional Directorate of Guayas Environment
Guayas (04) 232-0391 / (04) 230-0291

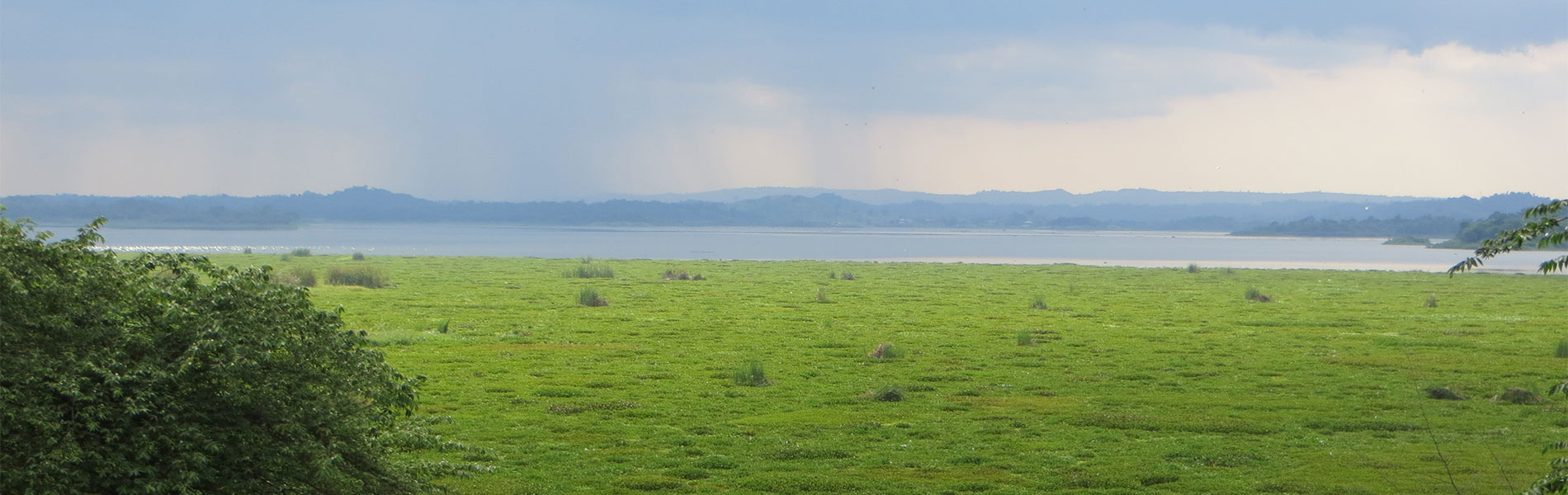
The lake is located in to west of Guayaquil the city, at kilometre 26 of the Guayaquil - Salinas road. It is an artificial reservoir that receives water from the Chongón and Perdido rivers, which originate in the coastal mountain range. The Chongón River receives water from the Guasmo, Aguas Negras, El Papagayo, Las Piñas and El Balsamo Marshes, before heading out tpwards the Pacific. You will often find sandbanks in the estuary, due to the high levels of sediment that the river carries down from higher altitudes. Corazon and Fragatas islands formed in this way, as is La Isla del Sol.

There is a public use area where activities such as hiking, bike rides, picnics and walking/running trails are availble. There is also a playground.

Culture, biodiversity and attractions
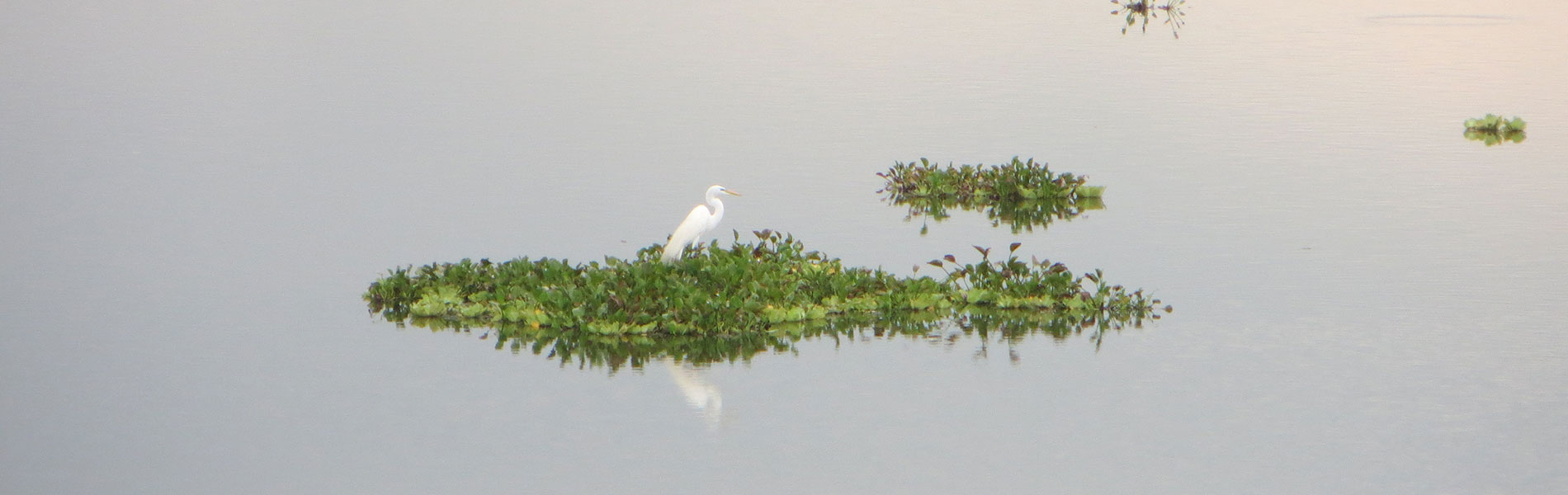
Although there are no villages within the recreational area, it has always been used and visited by nearby communities to collect firewood and for artisanal fisheries. The reservoir is an artificial ecosystem created less than 30 years and aquatic fauna that exists now comes from the rivers that feed it. You can find fish like the 'old blue' or the bocachico, which is considered good eating. Birdlife is also attracted to the reservoir, particularly waterfowl and migratory birds. More than 70 species are recorded, the most common of which include cormorants, herons, ducks and kingfishers. This recreation area offers a quiet environment good for family-based activities such as hiking, boating, bird watching, picnicking and bike rides.











