Description
Geography
Cultural
aspects
Biodiversity
Main
attractions
Activities
allowed
Existing
facilities
Documents and
recommendations
How to get?
The expansion of cities occurs often at the expense of natural ecosystems that surround them. In the case of Guayaquil , the growth of various urban and rural parishes has progressively taken over the mangrove ecosystem. For this reason, the remnants of the mangrove estuary in this area were protected through the creation of this reserve. Its importance lies not only in that it is vital for the flora and fauna of the Gulf area, but also by the great landscape and its aesthetic and recreational value - even more so becuase of its position within the largest and most populous city in the country.

This reserve is located in the city of Guayaquil and there are several ports along the Estero Salado.
Puerto Hondo. From Guayaquil traveling on the road to the coast, take the road that heads to Puerto Hondo at kilometre 17.5 which is where you enter to the offices of the reserve.
For more information contact the offices of the Provincial Directorate of Environment
Guayas (04) 232-0391

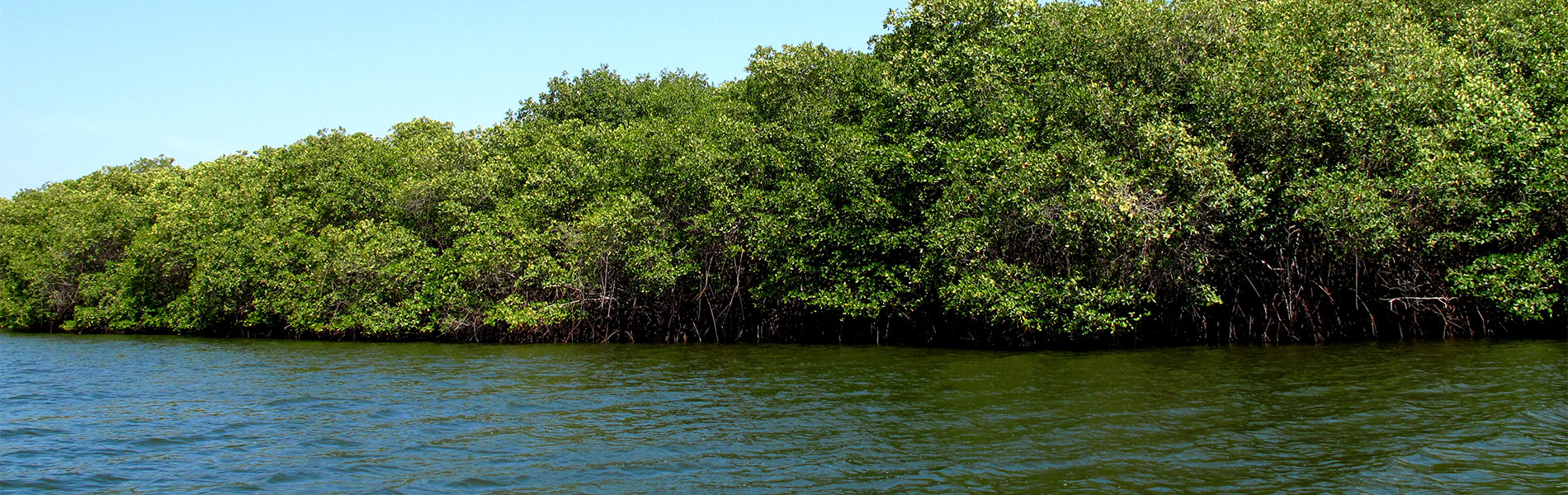
Mangroves El Salado, as it is also known , are named after the main estuary or inlet that exists in the Gulf of Guayaquil. The reserve is located in the northern gulf, in the inner part of the estuary , made up of several estuaries, canals and mangrove forests that are located west of the city. It also includes swamps located within the city, in neighborhoods like Miraflores, Urdesa and Kennedy.
The fresh water that feeds this area comes from the basin of the river Chongón and runoff from the hills of the city. Salt water, however, flows up the estuary and enters estuaries as Mongon, Plano Seco and El Salado.

NOTE: This area dosen’t have facilities for tourist visits yet ,but from the described areas, you can see the different areas of the mangroves. To explore the mangrove channels should talk to the Comuna Puerto Hondo.

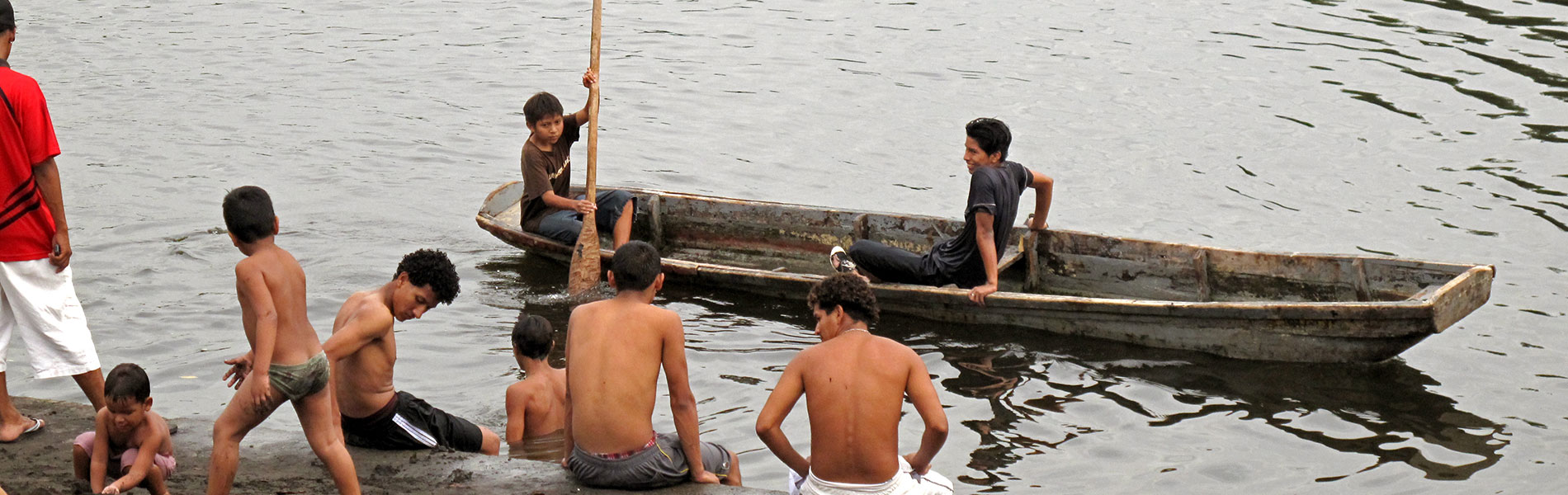
The history and development of the city of Guayaquil are closely linked to the ecosystems that grow around the Guayas River estuary, particularly the mangroves and channels that are in this protected area. During the first half of the twentieth century until about 1950, several sites that are within the reserve were important watering places for the Guayaquil population. At the same time , catching fish and shellfish harvesting were the main source of livelihood of fisherfolk. However, the development of the city and the installation of several factories and industries along its banks altered the natural characteristics of the estuary, hence why it was so important to protect.
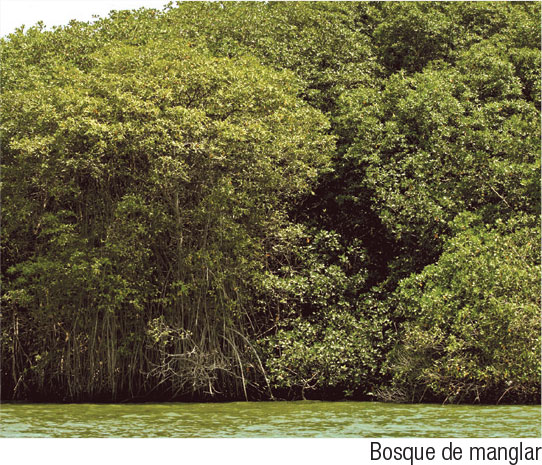

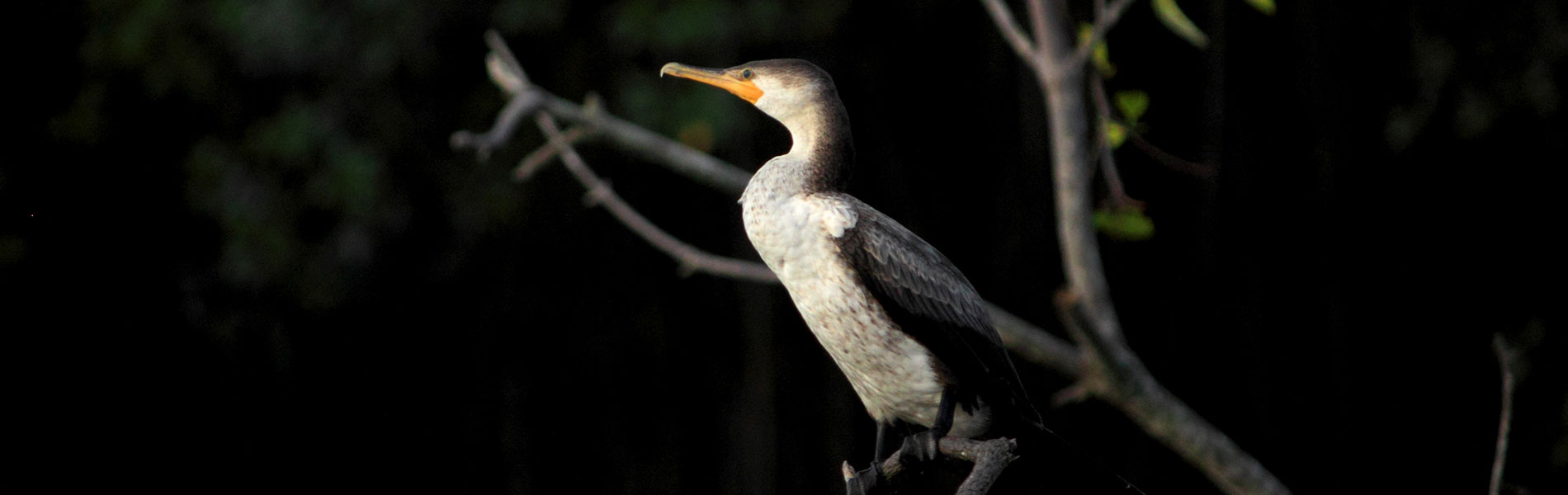
The nutrient-rich water of the estuaries and the environment that the mangrove roots create are ideal for species such as crabs, crabs, shells, oysters, mussels and shrimp. In addition, fish like catfish, bocachicos, bass and camotillos are numerous. The mangrove ecosystem is important for birdlife as a resting and nesting place. Take the opporuntity to watch the evening spectacle, when large numbers of herons come to rest in the branches. One of the most emblematic species of this reserve is the coastal crocodile. The status of its population is not known, but they are known to be very important players in terms of the ecological balanc eof the ecosystem. From colonical times to the first half of the twentieth century, expeditioners' books speak of the abundance of crocodiles on the banks of the rivers and estuaries of the Gulf; however, the demand for skin and fear of their attacks reduced their populations to near extinction. If you're lukcy (they are hard to spot) you might see mammals such as the crab-eating fox, river otter, the two-toed sloth or the little anteater.

This reserve includes some attractions that can be visited from different places, including some urban areas.
Parks and recreational areas of Guayaquil
Many parks and recreational areas of Guayaquil are located near the Salado estuary, where you can just wander and watch the birds. Among the areas with access to the estuary are; Malecón del Salado, Parques Lineales de la Avenida Barcelona, Avenida Carlos Julio Arosemen, of the University of Guayaquil and la Kennedy Norte, the Puente zigzag and small parks in North Urdesa.
Commune Puerto Hondo
Commune Puerto Hondo is designed to provide various services to visitors wishing to explore the mangrove channels . You can enjoy a natural spa, conduct guided tours and visit a Center for Environmental Education that where you can learn about species of migratory birds. There is a lookout for bird watching, food vendors, boat rentals and local guides.









